Vietnam – Asia’s New Manufacturing Hub? Export Landscape, Key Industries & Supply Chain Solutions
Vietnam is increasingly asserting its position as one of Asia’s new manufacturing hubs, thanks to its impressive growth rate, strategic location, and open trade policies. As global supply chains continue to shift and international businesses search for “China + 1” alternatives, Vietnam has emerged as a safe, flexible, and efficient manufacturing destination.
However, to fully capitalize on this opportunity, businesses must look beyond low labor costs. They need to understand Vietnam’s export structure by industry, assess its advantages and challenges, and adopt the right strategies to operate a reliable, optimized local supply chain.
The following article provides a comprehensive and up-to-date picture — backed by official statistics and practical solutions from Vietnam Agent — a trusted partner that supports global brands in managing supply chains across Vietnam.

I. Vietnam’s Economic and Trade Overview
1. Regional-Leading GDP Growth
- In Q2 2025, Vietnam’s GDP grew by 7.96%, surpassing expectations, driven by strong exports and FDI inflows.
- In 2024, GDP reached 7.09%, raising the country’s economic value to USD 476.3 billion.
- World Bank forecasts GDP growth in 2025 at 6.5–6.8%, outpacing Thailand and Indonesia.
2. Record-Breaking Trade Volume
- Total import-export turnover in 2024 reached USD 786.3 billion, with exports accounting for USD 405.53 billion.
- In Q2 2025: exports reached USD 116.93 billion, imports USD 112.52 billion, yielding a trade surplus of USD 4.41 billion.
- Trade-to-GDP ratio approached 200% — one of the highest globally.
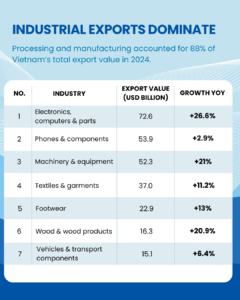
3. Industrial Exports Dominate
Processing and manufacturing accounted for 88% of Vietnam’s total export value in 2024.
4. Agriculture & Aquaculture Remain Strategic
- Vietnam exported over 1.62 million tons of Robusta coffee in 2024, making it the world’s second-largest exporter.
- Seafood (especially shrimp and pangasius) plays a major role in exports, especially to Japan, the EU, and the U.S.
5. Rising Regional Position
- Financial Times has dubbed Vietnam “the rising star of the global supply chain.”
- With political stability, a young workforce, and open trade policies, Vietnam is expected to maintain strong growth momentum for the next decade.
II. Key Export Industries – Opportunities and Highlights
Vietnam’s export growth is not driven by a single sector, but by a broad and balanced surge across many industries — from electronics, textiles, and wood products to agriculture and aquaculture. Each sector has its own strengths and specific characteristics that businesses should pay attention to when setting up production in Vietnam.
1. Electronics – the country’s leading export industry
- Vietnam is one of the largest manufacturing hubs for electronic components and devices in the region, thanks to strong investments from corporations such as Samsung, LG, Intel, and Foxconn.
- The export value of electronics (including phones, computers, components, etc.) exceeded 178 billion USD in 2024, accounting for more than 40% of total merchandise export turnover.
- Opportunities: ready supply chain, skilled technical workforce.
- Note: some high-tech components still need to be imported; dependency on the industrial cluster of Bac Ninh – Thai Nguyen – Hai Phong.
2. Textiles and Footwear – traditional strengths
- As labor-intensive industries, textiles and footwear consistently rank among the top five largest export sectors, with total export turnover nearing 60 billion USD.
- Vietnam is currently the third-largest textile exporter in the world (after China and Bangladesh).
- Main production centers: Ho Chi Minh City, Binh Duong, Dong Nai, Nam Dinh, Thai Binh.
- Challenges: lack of domestic materials; strict rules of origin to access tax incentives.
3. Wood and Wood Products – strong presence in the U.S. and EU markets
- Export of wood and wood products in 2024 reached more than 16 billion USD — mainly furniture, tables, chairs, cabinets, doors, pallets.
- Vietnam is the second-largest wooden furniture exporter in the world (after China).
- Advantages: sustainable plantation wood sources, skilled labor, modern production lines.
- Risks: strict requirements for legal wood certification (FSC, PEFC), compliance with anti-dumping regulations.
4. Aquaculture – a key strength in the Mekong Delta and Central Coast
- Total seafood export turnover exceeded 9 billion USD, with shrimp and pangasius as two main export items.
- Vietnam is the second-largest shrimp exporter in the world.
- Strengths: vast natural farming areas, advanced cold-chain processing technology.
- Note: strict control of antibiotic residues and traceability required by demanding markets like the EU and the U.S.
5. Agricultural Products – coffee, cashew, pepper, fruits
- Vietnam ranks among the world’s top exporters of Robusta coffee, cashew nuts, and black pepper.
- Fruit exports (especially durian, banana, lychee) to China and South Korea have increased sharply thanks to signed quality protocols.
- Large potential, but strict control of quality and technical standards is needed to access developed markets in the long term.
III. Vietnam’s Strategic Advantages in the Global Supply Chain
1. Strategic geographic location – multidirectional connectivity
- Located between China, ASEAN, and the Pacific, Vietnam is well-positioned to connect trans-Asia supply chains — particularly through major seaports such as Hai Phong, Cai Mep – Thi Vai, and Cat Lai.
- Its geographic proximity to consumer markets like Japan, South Korea, and Australia helps shorten shipping times and reduce logistics costs.
2. Extensive network of free trade agreements (FTAs)
- Vietnam is currently one of the few countries simultaneously participating in multiple next-generation FTAs: CPTPP, EVFTA, RCEP.
- As a result, goods manufactured in Vietnam have access to more than 50 markets with outstanding tariff preferences.
- However, to take advantage of FTAs, businesses must strictly comply with rules of origin — especially regarding the localization rate and the origin of materials.
3. Competitive production costs — but shifting
- Vietnam’s average labor costs remain lower than those in China, Thailand, and Malaysia, but are gradually increasing in major industrial zones.
- A new trend: many international businesses are relocating factories to provinces such as Nghe An, Quang Nam, and Hau Giang to save costs and more easily recruit labor.
4. Political stability and flexible FDI attraction policies
- Vietnam consistently maintains stable credit ratings from organizations such as Moody’s, S&P, and Fitch.
- The government is actively reforming administrative procedures, shortening investment registration time, and offering tax incentives for high-tech and environmentally friendly manufacturing projects.
IV. Existing Challenges in Vietnam’s Manufacturing Sector
Although Vietnam has many advantages, it still faces several barriers that require thorough preparation before expanding production.
1. Inconsistency among factories
- Vietnam has tens of thousands of manufacturing facilities, but not all are ready for mass production, stable quality, or high documentation and compliance standards.
- Many small factories have yet to adopt automation, lack standardized quality control procedures, and are unfamiliar with rules of origin or the technical requirements of the EU/US markets.
2. Fragmented supply chain management system
- Many factories rent third-party workshops and outsource parts of their production processes without transparency.
- This makes it difficult for international businesses to manage the entire process — from raw materials and semi-finished goods to packaging.
3. Lack of clear origin documentation
Many orders are denied tariff incentives even though they are produced in Vietnam because:
- The BOM does not meet intra-regional content thresholds.
- Documentation proving raw material origin is incomplete.
- PO management and production records are inconsistent.
This poses a major risk for businesses intending to take advantage of FTAs like EVFTA and CPTPP.
V. Global Manufacturing Shift & Vietnam’s Rising Role
1. “China + 1” is no longer a trend — it’s a strategy
- Many major brands are diversifying their supply chains and no longer placing their entire production in China.
- Vietnam, along with India and Mexico, has emerged as a top destination thanks to:
✅ More competitive costs
✅ Easier market access to the U.S. and EU through FTAs
✅ Policy reliability and efficient logistics
2. Global brands have already moved to Vietnam
- Samsung, LG, Foxconn, Nike, Adidas, Intel, Lego… have all made major investments in Vietnam.
- Example: Foxconn has committed to expanding iPad and MacBook production in Bac Giang; Lego is building its first carbon-neutral factory in Binh Duong.
- The supporting industry is also accelerating, making it easier for new brands to join the supply chain.
3. Vietnam is becoming ASEAN’s strategic production hub
Vietnam is not just a subcontracting site — it’s gradually enhancing its position by:
- Increasing material localization
- Improving manufacturing technology
- Developing specialized industrial clusters (e.g. electronics in the North, textiles in the Central-South regions)
VI. How to Choose the Right Factory in Vietnam?
Placing a production order in Vietnam is easy. But ensuring the order meets standards, timelines, and legal requirements is another story.
International businesses need to clarify the following factors before signing any partnership:
1. Assess production capability
✅ Can the factory meet the required production volume?
✅ Does it have sufficient workforce and machinery for continuous production — or only for sample making?
2. Verify the operating model
✅ Does the factory outsource any stages? If so, which parts are done in-house and which are outsourced?
✅ Can material origin be traced? Has the factory previously exported goods — and to where?
3. Set up and monitor a custom process
✅ Each business needs a tailored production process — from BOM, lead time, QC checklist, to packaging visuals.
✅ Can you monitor each order? Or will you only find out the results when the goods are in containers?
4. Ensure contract compliance & export legality
✅ Are there clear contract terms regarding delivery schedule and output quantity?
✅ Does the factory have the capacity to handle documentation for tax incentives (CO form EUR.1, RCEP, CPTPP)?
✅ Do they understand the technical standards of the target market?
VII. Vietnam Agent – End-to-End Supply Chain Solution in Vietnam
Vietnam is a fertile production ground — but difficult to navigate without a local team.
From differences in production processes, communication culture, to legal frameworks and quality control — many global brands have paid the price for failing to manage remote production effectively.
Vietnam Agent exists to solve that problem.
With an extensive network across key industrial provinces such as Bac Ninh, Hai Phong, Binh Duong, Ho Chi Minh City, Dong Nai, Long An…, Vietnam Agent helps international businesses establish, control, and optimize their entire supply chain in Vietnam.
1. Direct access to factories and their satellite ecosystems
- We help clients directly access the most suitable factories, both OEM and ODM — with no intermediaries.
- Conduct full assessments of production capacity, machinery, line speed, and scalability
- Analyze the surrounding supply chain: sub-suppliers, subcontractors, packers, logistics — to ensure synchronization and long-term stability
2. Customized production roadmap per industry
- Each sector has its own specifics — from design, technical precision, storage conditions to delivery timelines.
- Vietnam Agent designs a bespoke production process for each order — based not only on attractive samples or low cost, but on actual capabilities and operational KPIs.
- Example: In furniture, we distinguish between factories specialized in MDF, solid wood, or both; in textiles, we differentiate between sample-only units and those ready for mass production.
3. Quality control at every critical checkpoint
- Inspect raw materials, sample during production, approve before packing — following client-specific standards
- Deploy technicians directly to factories during key phases like sample approval or pre-shipment inspection
- Use a live reporting system by PO — including photos, checklists, videos, and transparent documentation
4. Supply chain management — from contract to delivery
- Draft contracts with clear terms on quantity, lead time, and quality responsibilities
- Negotiate payment terms aligned with local practices, reducing credit risk
- Coordinate the entire logistics process: from container booking, in-factory loading, to customs clearance for export
5. Legal compliance and intellectual property
- Support contract registration and IP protection in Vietnam
- Review all legal conditions related to FTAs and origin rules — especially important for clients seeking tax incentives
- Ensure terms on confidentiality, non-replication, and no post-contract production are fully enforced
Vietnam Agent doesn’t just find you a factory — we manage your entire production process in Vietnam.
From the first sample to the final shipment, we help you produce with confidence, transparency, and efficiency.
VIII. Conclusion – Vietnam Is a Strategic Opportunity, But Not a Plug-and-Play Market
Manufacturing in Vietnam is a strategic opportunity — not just to cut costs, but to diversify supply chains, access new consumer markets, and leverage rare trade advantages.
However, opportunity only becomes a competitive edge when the business can manage effectively.
Differences in production methods, operational culture, legal requirements, and technical standards demand a clear strategy — and a trusted local partner.
Vietnam Agent is your reliable partner, helping international brands:
- Quickly access real, transparent, and trustworthy factory networks
- Establish custom production processes for each product category
- Monitor quality and progress on-site — without the need for a resident team
- Reduce risks in contracts, legal matters, IP, and origin rules
- Operate manufacturing in Vietnam with flexibility, efficiency, and transparency
Whether you’re looking to shift part of your capacity from China, searching for a new factory for a strategic category, or simply want to understand Vietnam’s manufacturing ecosystem better — we can help.
📩 Contact Vietnam Agent
Start with a conversation — and let Vietnam Agent help you build sustainable manufacturing capabilities in Vietnam: https://lnkd.in/dxUrvy8V